728x90
중앙대학교 3-2 리눅스 응용 설계 (손용석 교수님) 과목 정리입니다.
Task Group and Task Scheduling Entity
Only Considering Fairness of Tasks
- task의 관점에서 CPU allocation은 공정하다.
- user의 입장에서는 CPU allocation이 공정하지 않다.

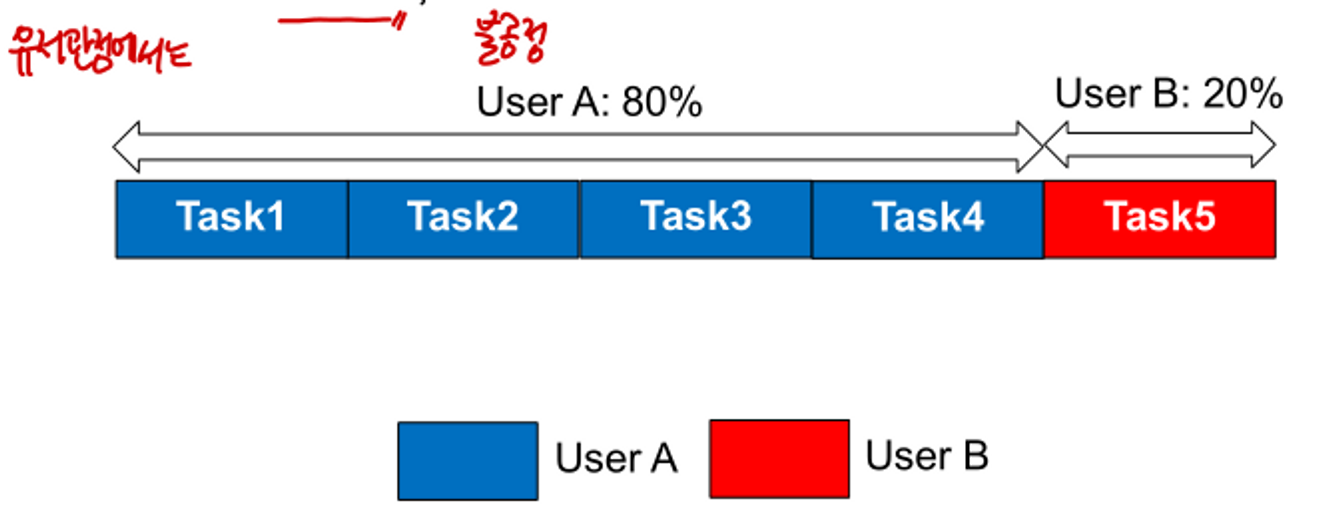
- CFS는 task group이 user 사이의 fairness를 보장하도록 지원해야 한다.
- task group은 task 뿐만 아니라 다른 task group도 포함할 수 있다.
Task scheduling entity
- scheduling의 단위로서 task와 task group을 모두 지원하기 위해 scheduling entity의 개념이 도입되었다.
- task 나 task group을 scheduling 할 때
- task_message structure 또는 task_group structure를 직접 queue에 넣지 않고 scheduling entity를 삽입한다.

Scheduling Entity

- load_weight : scheduling entity의 load weight
- rb_node : scheduling entry가 tree에 삽입될 때 사용되는 tree node
- group_node : runqueue는 삽입된 normal task의 entity list를 cfs_tasks list를 사용하여 저장한다.
- on_rq : 해당 entity가 enqueue 되었는지, 아닌지
- 1이면 run queue에 삽입되었고, 이 entity가 current entity이다.
- 그 외 0
- exec-start : 가장 최근에 실행된 시간
- sum_exec_runtime : 총 실행 시간
- nr_migration : CPU migration 횟수 (load balancing mechanism 횟수)
- depth : scheduling entity hierarchy
- cfs_rq : 자체 CFS (task group을 위한 것)
Scheduling Entity and Red-Black Tree

When is Scheduling performed?
1. periodic scheduling이 timer interrupt를 사용한다.
- timer interrupt에 의해 current task가 preempt 되었는지 아닌지를 주기적으로 체크할 수 있다.
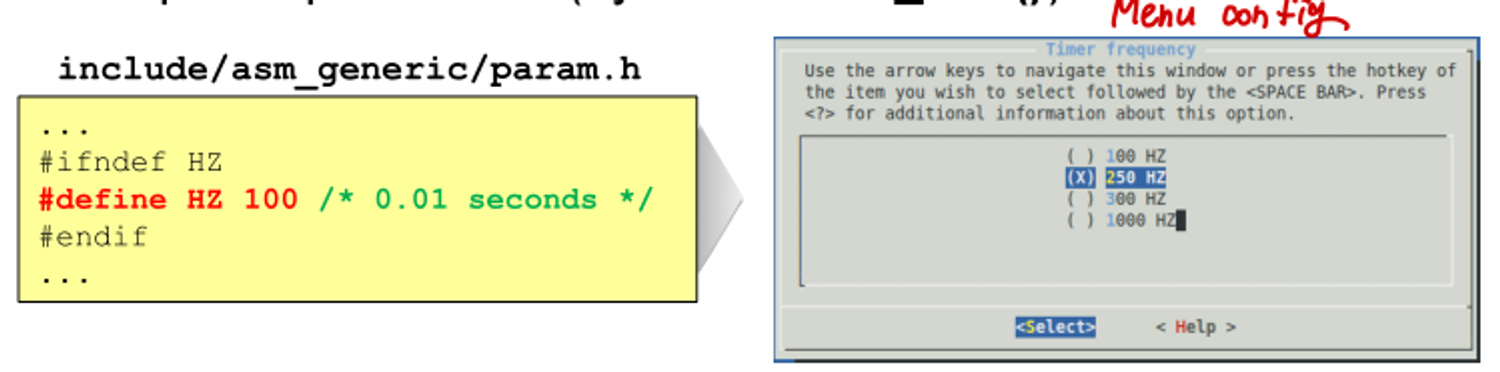
2. event-driven scheduling
- 명시적으로 schedule()을 호출한다.
⇒ 모두 scheduling을 위해 schedule()을 호출한다.
Periodic Scheduling using timer interrupt
periodic scheduling은 task의 반응성을 보장하는 mechanism
- time interrupt가 주기적으로 생성된다.
- 실행중인 task가 멈추고 timer interrupt handler function이 실행된다.
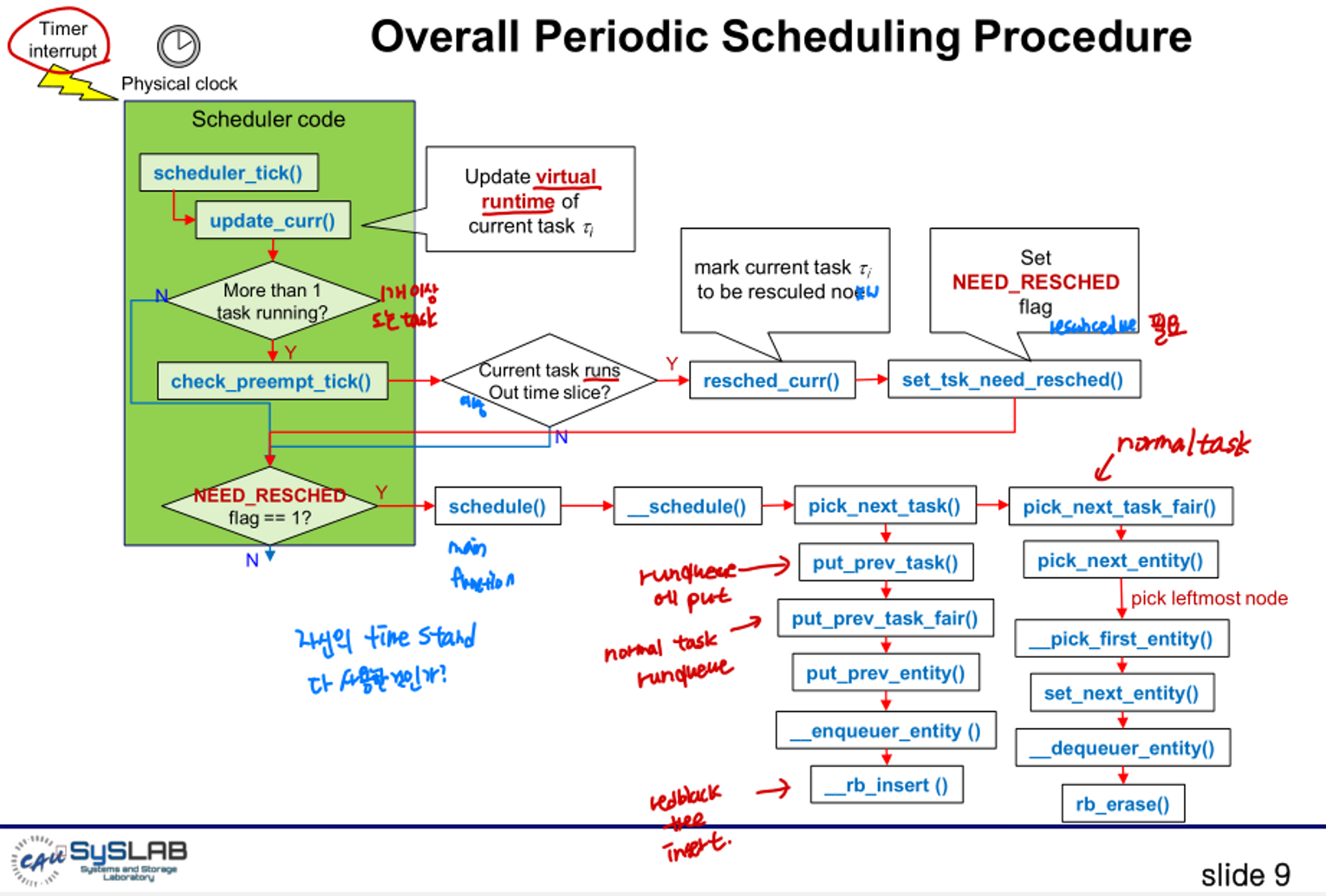
- task는 scheduler_tick()을 실행한다.
- task가 할당된 time slice 전부를 사용했는지 아닌지 확인한다.
- 모든 time slice를 사용했다면 scheduling을 요청하기 위해 task는 TIF_NEED_RESCHED flag를 세팅한다.
- task가 interrupt processing을 마치고, scheduling 요청이 있었는지 확인한다.
- scheduling 요청이 있었다면, task는 scheduling을 위해 schedule() 을 호출한다.
Periodic Scheduling with scheduler_tick()

- smp_processor_id() : core id를 가져온다.
- cpu_rq() : core의 runqueue를 가져온다.
- rq→curr : 현재 실행중인 task를 가져온다.
- raw_spin_lock : spin lock
- update_rq_clock() : runqueue의 clock field가 recent value로 변경된다.
- curr_sched_class→task_tic(rq, curr, 0) : current task의 execution time을 업데이트하고, current task가 모든 시간을 사용한 경우 flag 세팅
- update_cpu_load_active : runqueue의 load를 업데이트한다. load balancing을 수행할 때 run queue에 있는 load와 사용되고 있는 load를 나타낸다.
- raw_spin_unlock : release lock

- if (cfs_rq → nr_running > 1) : time slice가 consume 되었는지 확인
- 필요한 경우 새롭게 실행된 task로 preempt
update_curr(): Updating Runtime and Virtual Runtime

- rq_clock_task : run queue의 현재 시간 가져오기
- delta_exec = now - curr→exec_start : task의 actual 실행시간 가져오기 → one tick period
- curr→exec_start = now : task 시작 시간을 업데이트한다.
- curr→sum_exec_runtime += delta_exec : total execution time에 delta_exec를 추가한다.
- curr→vruntime += calc_delta_fair(delta_exec, curr) : delta를 current task의 vruntime에 추가한다. 현재 task의 vruntime을 계산하는 것
- update_min_vruntime(cfs_rq) : vruntime 업데이트
check_preempt_tick(): Check preemption

- sched_slice() : current task의 time slice 계산
- execution time의 time slice 비교
resched_curr(): Rescheduling current

- set_tsk_need_resched() : task가 rescheduling이 필요한지 확인
test_tsk_need_resched(): check whether it needs to schedule

set_tsk_need_resched(): set this task to be rescheduled

- set_tsk_thread_flag() : 입력된 flag로 flag를 세팅한다.
Inter Processor Interrupt
IPI (Inter Processor Interrupt)
- IPI는 interrupt의 special type
- multiprocessor system에서 interrupt processor가 다른 processor의 동작을 필요로 하는 경우 한 processor가 다른 processor를 interrupt할 수 있다.


When is Scheduling performed
Event-driven scheduling
- 기다리는 task가 wakeup API를 통해 깨어났을 때, scheduling이 가능한지 체크

- preemption now : 선점 가능
- wakeup의 scheduling class가 current task보다 더 높으면 preemption
- current task와 wakeup task의 scheduling class가 동일하고, current task의 vruntime이 wakeup task보다 큰 경우 preemption
- Do not preemption now : 선점 불가
- wakeup task의 scheduling class priority가 낮을 때
- wakeup task의 vruntime이 current task vruntime보다 큰 경우
- Event driven scheduling이 일어나는 경우
- task가 명시적으로 CPU를 양보하는 경우
- 우선순위가 높은 task가 run queue로 이동되는 경우
- task의 우선순위가 변경되는 경우
- task의 scheduling class가 변경되는 경우
- 새로 생성된 task를 먼저 실행해야 하는 경우

- Sleep API를 호출할 때
- 실행 중인 task는 sleep API를 호출함으로써 wait state에 진입하고, condition이 만족되었기 때문에 CPU를 사용할 필요가 없다.
- schedule() 은 CPU를 사용할 수 있는 다른 task에 의해 호출된다.

- Preemption이 가능해진 후 (preempt_enable())
- preemption이 불가능한 경우, 실행되지 못한 task의 delay time이 증가한다.
- delay time을 가능한 한 줄이고 싶은 경우, scheduling이 kernel preemption이 가능할 때 시도되어야 한다.
- sleep API 대신 __schedule() 함수를 바로 호출한다.

- interrupt handling이 끝난 후에, scheduling이 필요한지 아닌지 체크
Schedule()

- scheduling은 scheduling request가 없을 때까지 진행한다.
- disable preemption
- schedule() 호출
- 적절한 next task를 선택하면 task switching이 수행된다.
- 매개변수로 false를 전달하면, scheduling이 preemption을 활성화하고 시작되지 않는다는 것을 의미한다.
- current task가 명시적으로 wait state인 경우 (sleep 등), scheduler는 run queue에서 task를 가져온다.
- true인 경우 schedule function은 dequeue를 수행하지 않는다.
728x90
'School Lecture Study > Linux System Application Design' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 8. Linux Kernel Data Structure (0) | 2022.12.20 |
|---|---|
| 7-4. Task Scheduling in Linux (4) (0) | 2022.12.20 |
| 7-2. Task Scheduling in Linux (2) (0) | 2022.12.20 |
| 7-1. Task Scheduling in Linux (1) (0) | 2022.12.20 |
| 6-4. Synchronization (4) (0) | 2022.12.20 |