728x90
8. Linux Kernel Data Structure
중앙대학교 3-2 리눅스 응용 설계 (손용석 교수님) 과목 정리입니다.
Kernel Data Structure
- kernel data structure는 current state와 system의 정보를 저장할 때 매우 중요하다.
- Example
- Red-black tree는 scheduling entity 관리
- Linked list는 file system의 transaction 관리
- kernel data structure는 오직 kernel과 kernel의 subsystem에 의해서만 접근 가능하다.
- data structrue는 다른 data structure와 system data를 가리키는 pointer를 포함한다.
- 때때로, data structure performance가 전체 system의 performance를 결정할 수도 있다.
- Example
- Kernel data structure
- Linked list
- Red-black tree
- Hash table
- Xarray
- etc
Limitation of Previous Linked List
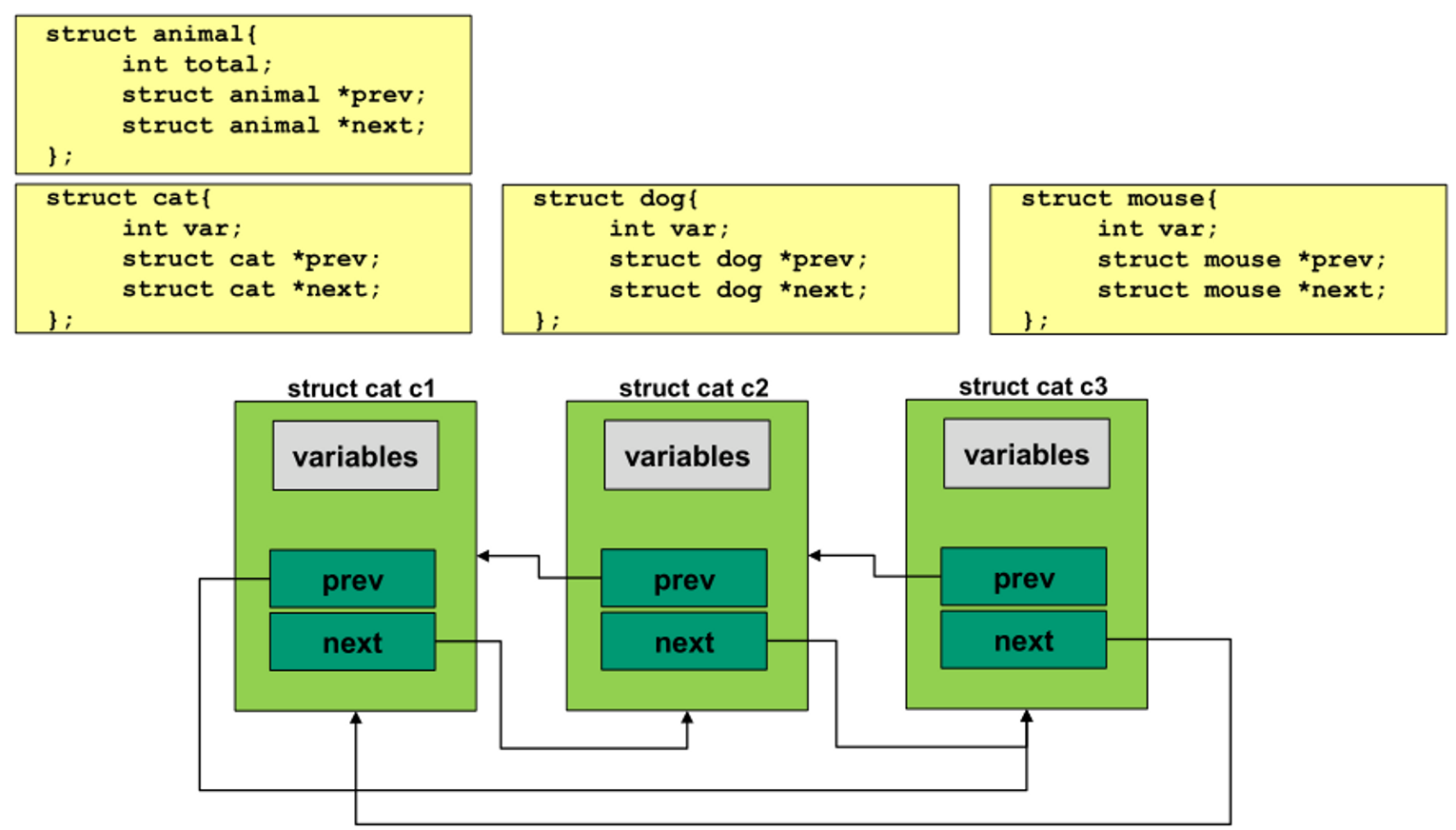
- animal Linked list를 만들 때, 다 각각 구조체 포인터 prev, next를 갖는다.
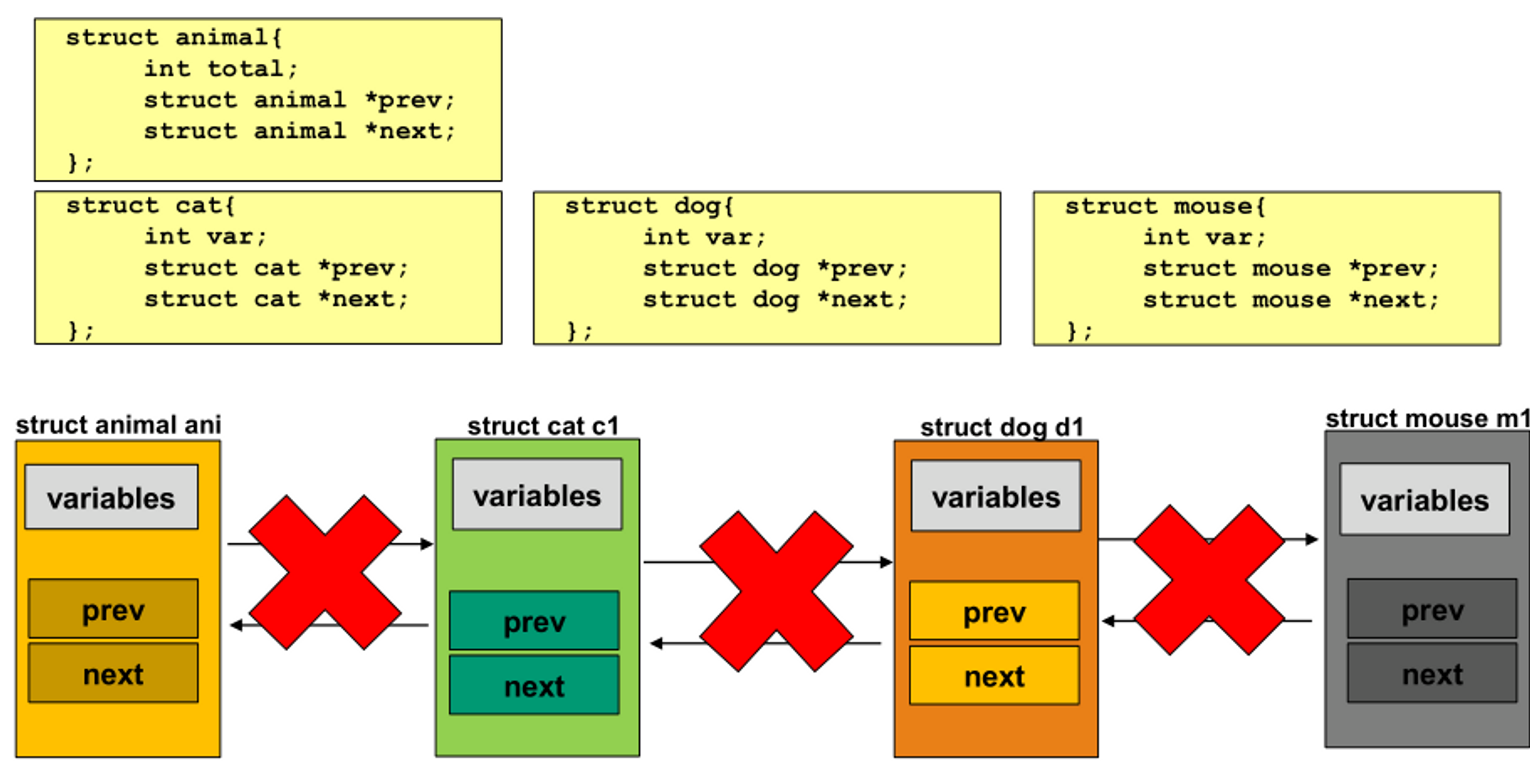
- 그러나 위처럼 구현하면 animal과 cat, dog, mouse는 서로 연결될 수 없다.
- 구조체 자료형이 다르기 때문에
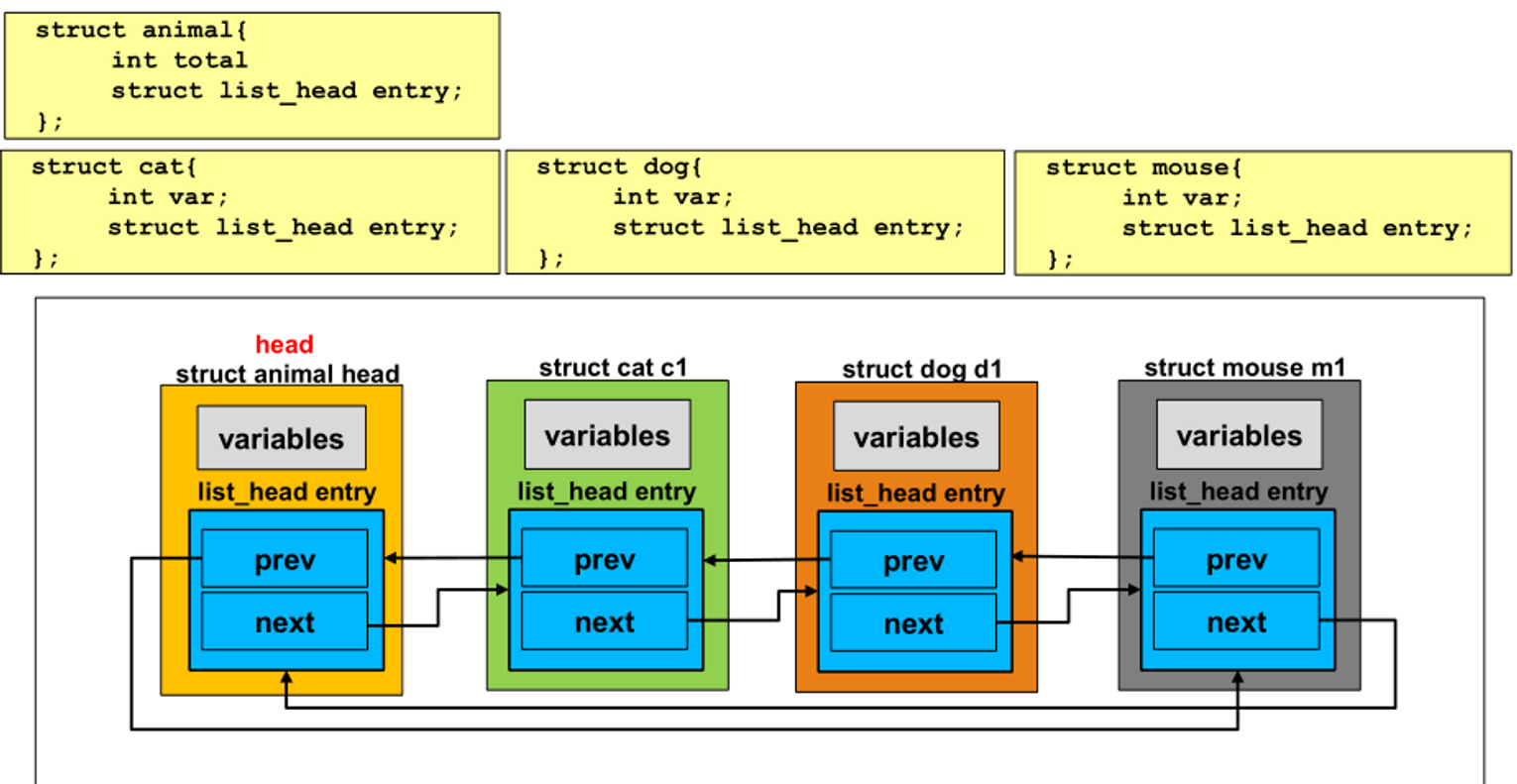
- linked list는 구조체 자료형과 관련 없이 연결할 수 있어야 한다.
- → list_head 자료형으로 변경
Linked List
Initialization of Linked List
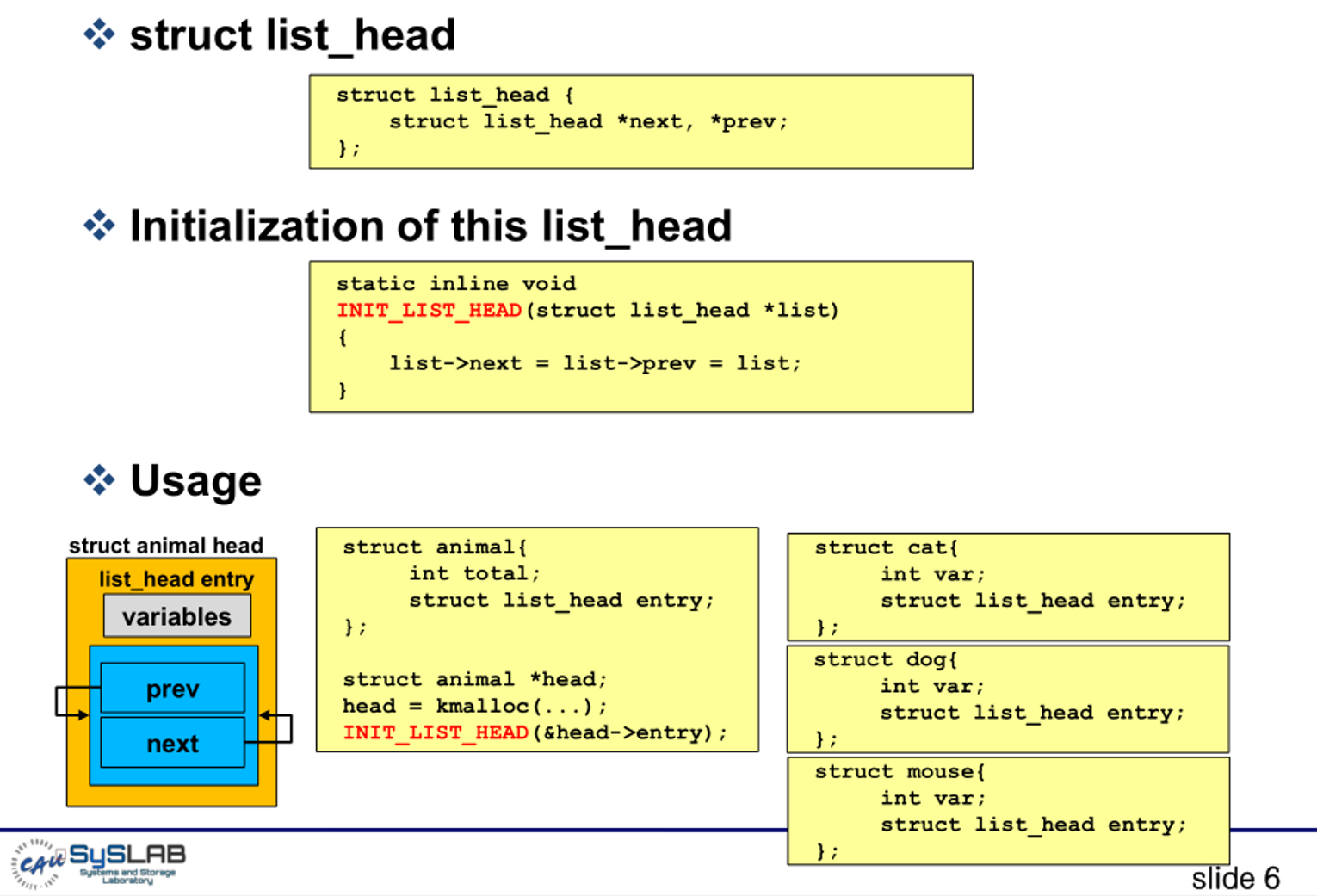
- list_head 자료형에는 list_head *next, *prev 포함
- INIT_LIST_HEAD : 지역 변수 list_head 초기화
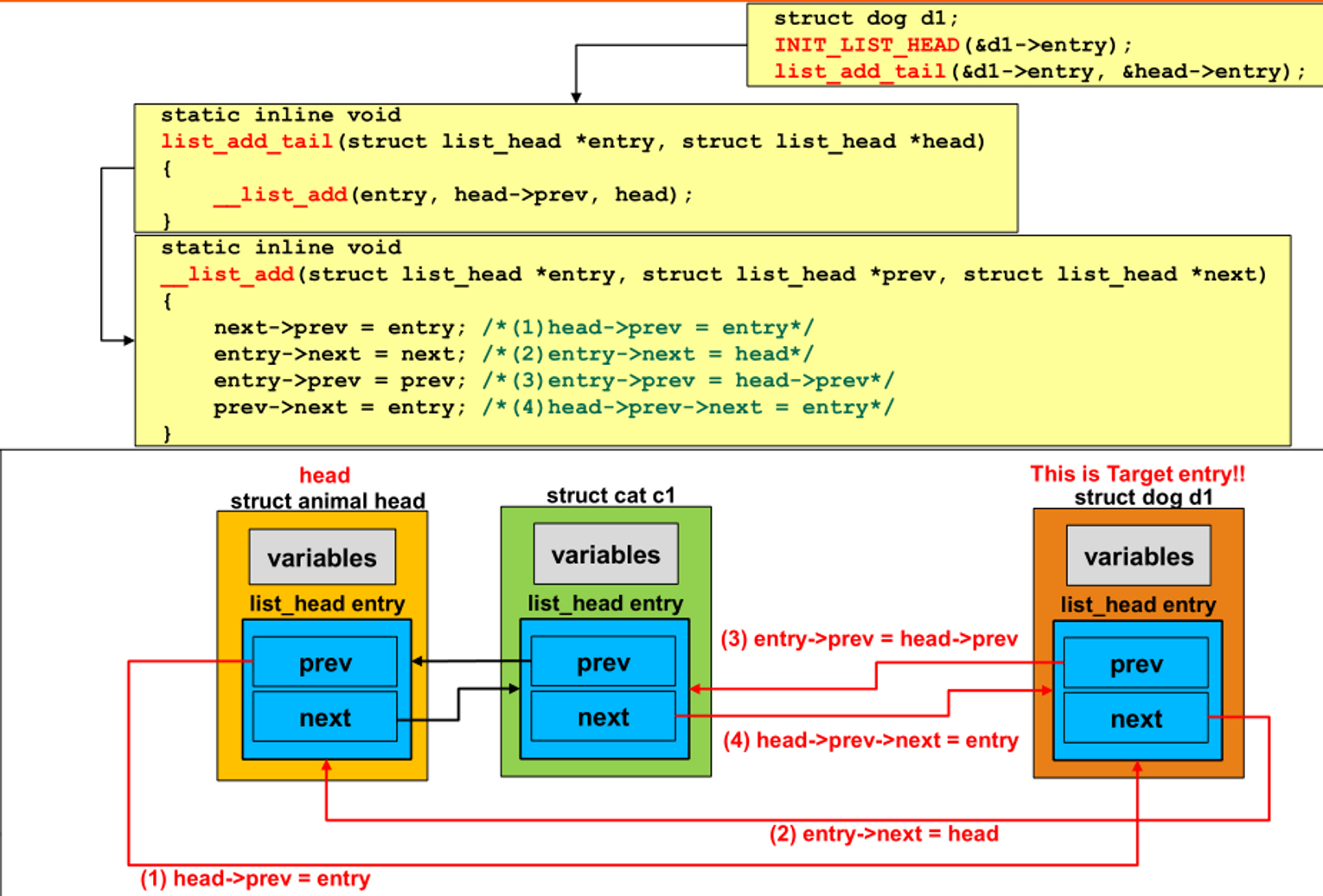
list_add_tail() : add an entry to tail of list
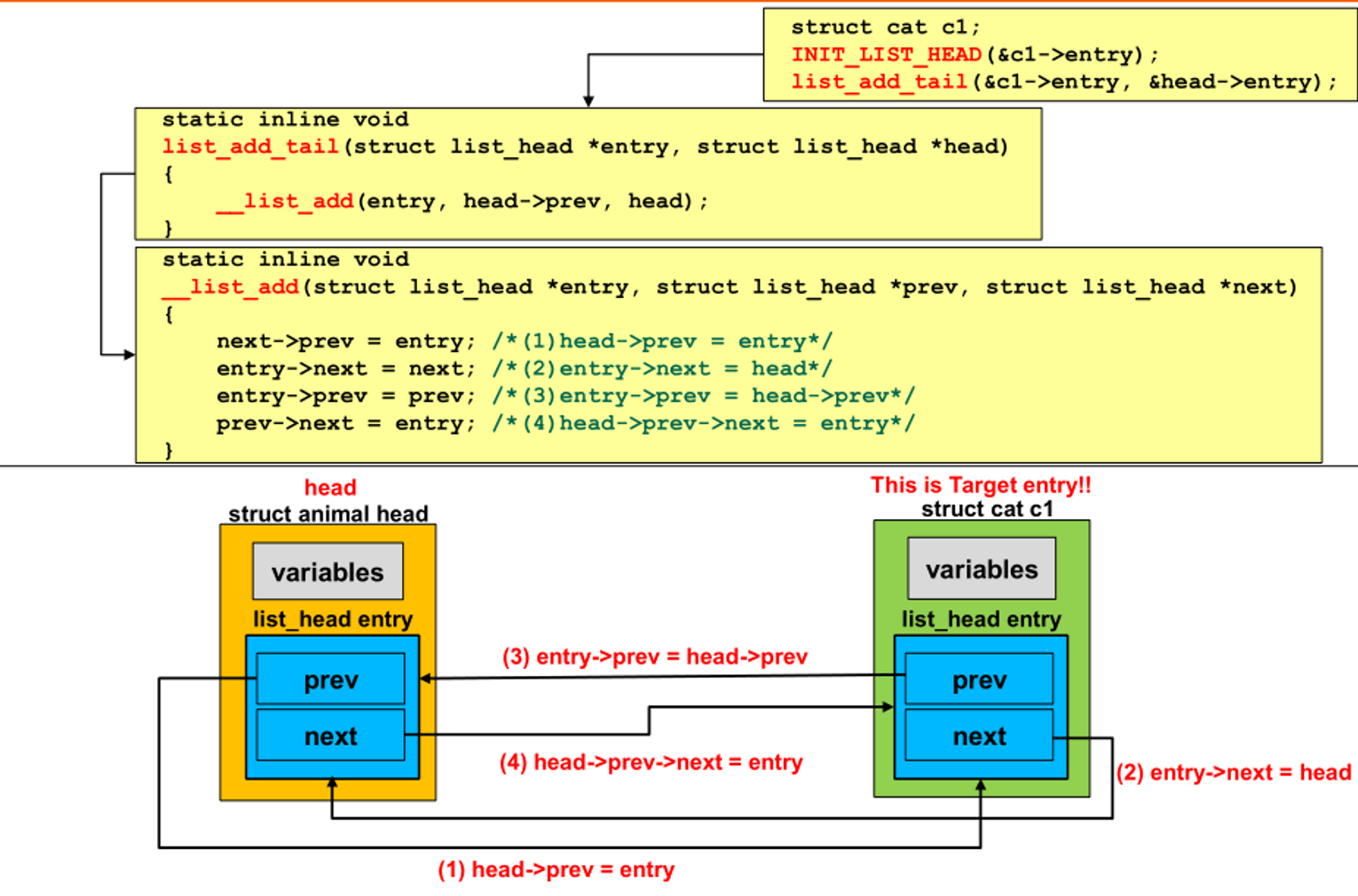
- __list_add() 호출
- __list_add
- head의 prev를 add할 node로 설정
- add할 node의 next는 head
- add할 node의 prev는 head의 previous node
- head의 previous node의 next는 add할 node
list_del() : delete an entry
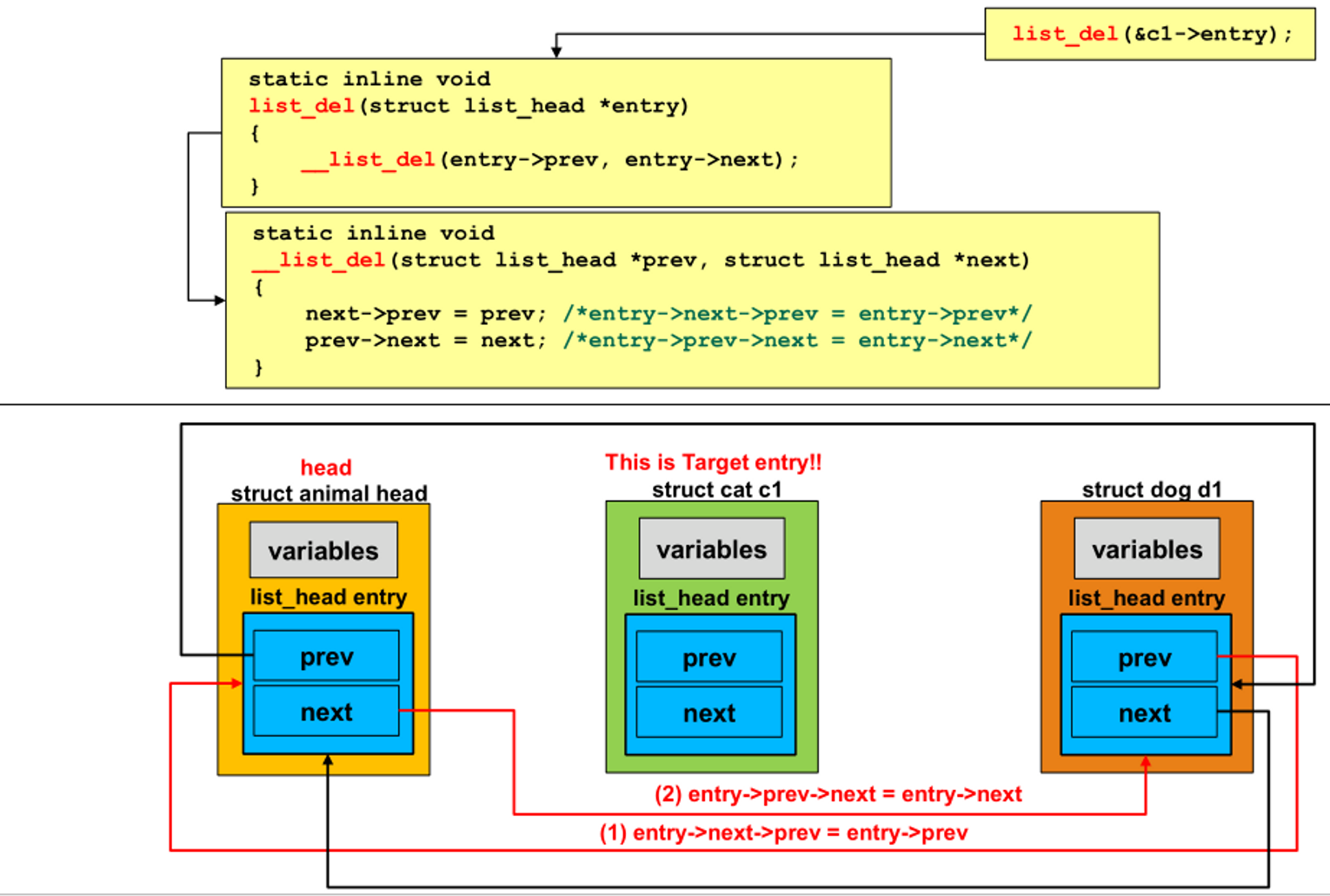
- __list_del() 호출
- __list_del : 지울 노드를 entry라고 한다.
- entry의 다음 노드의 previous는 entry의 이전 노드
- entry의 이전 노드의 next는 entry의 next
Lock based Linked List
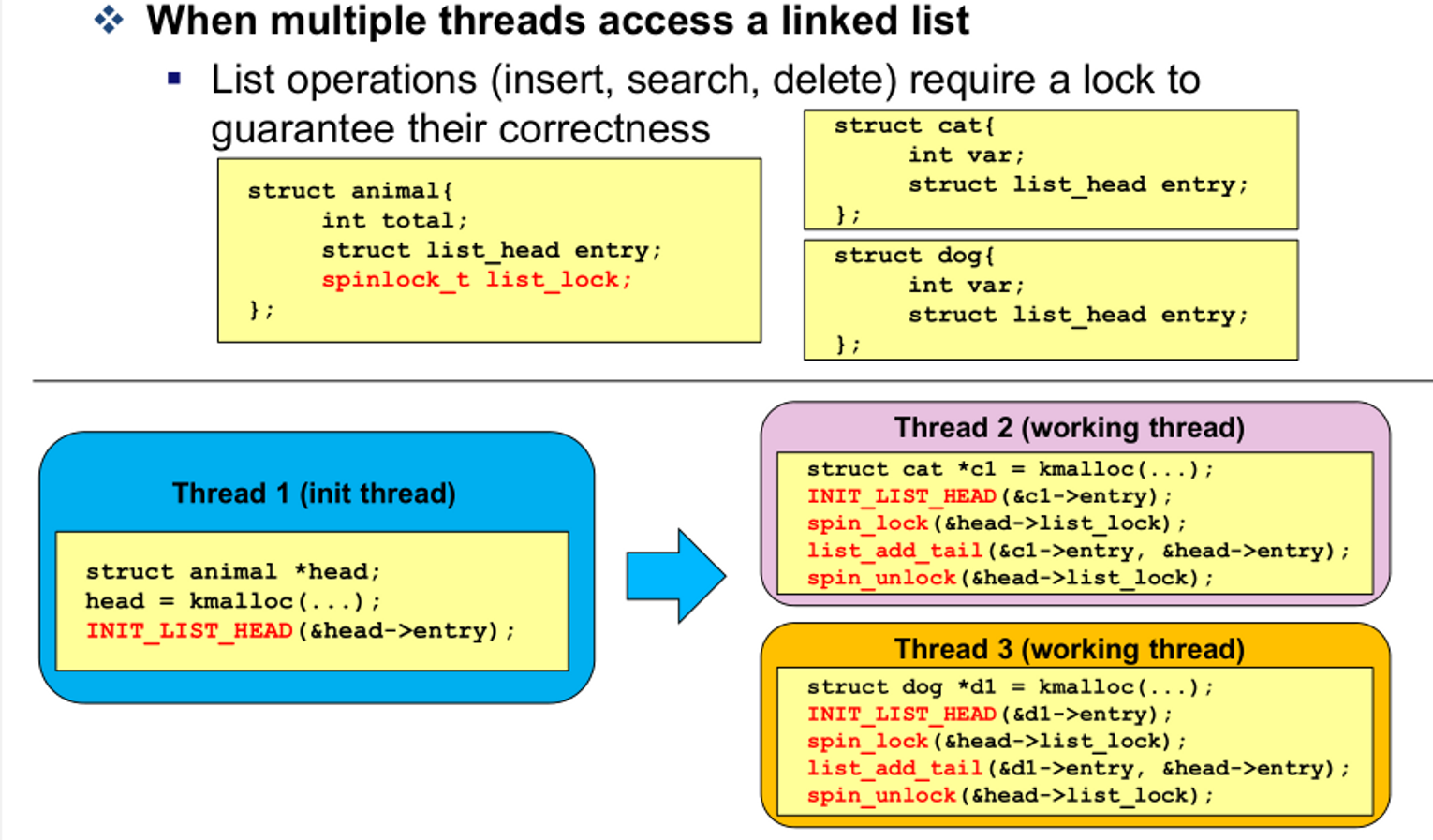
- linked list에 여러 thread가 접근할 때
- list operation은 correctness를 보장하기 위해 lock이 필요하다.
- insert, search, delete할 때 모두 spin_lock 사용
Lock-free linked list
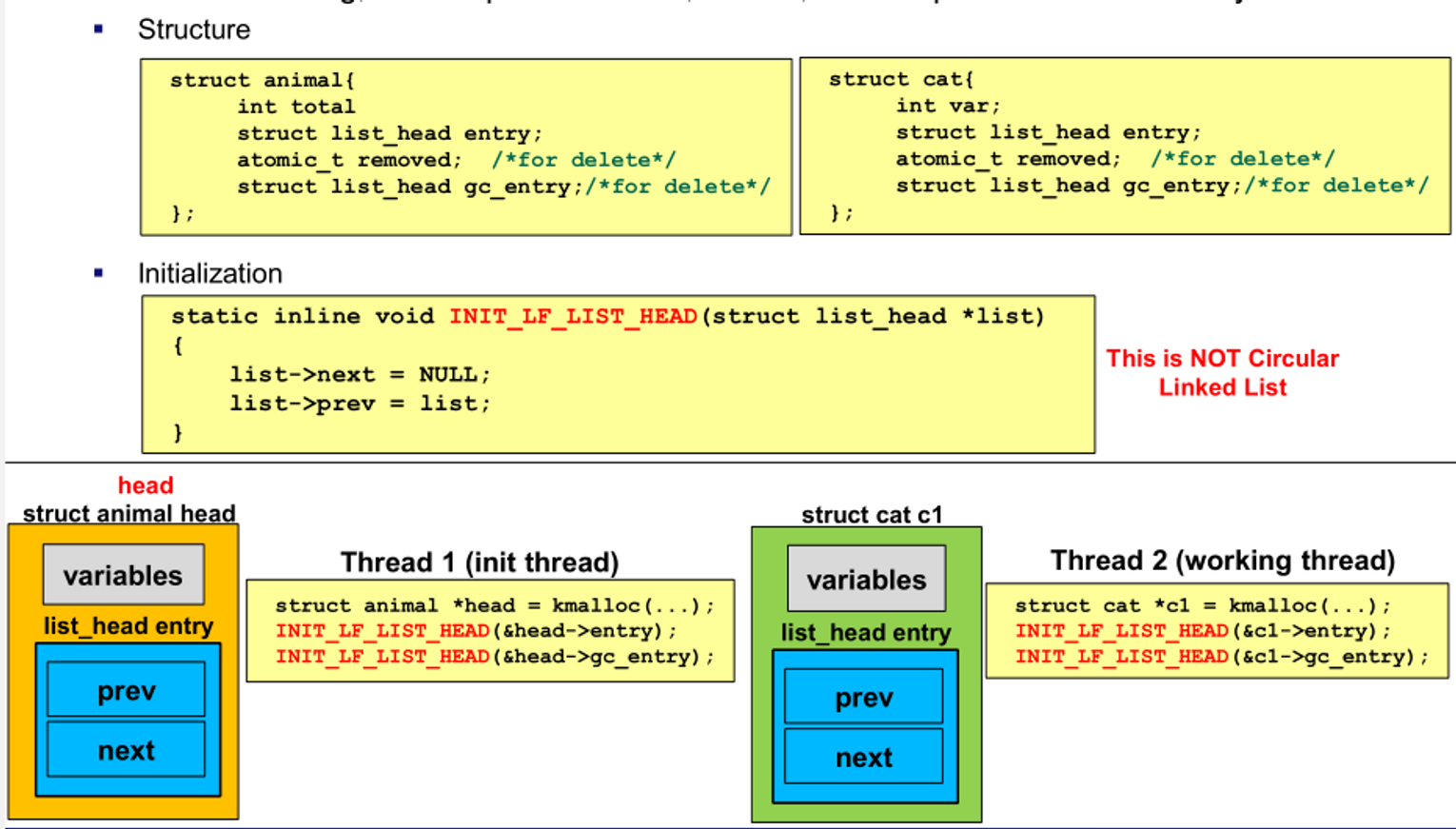
- circular linked list 사용하지 않음
Initialization head and tail
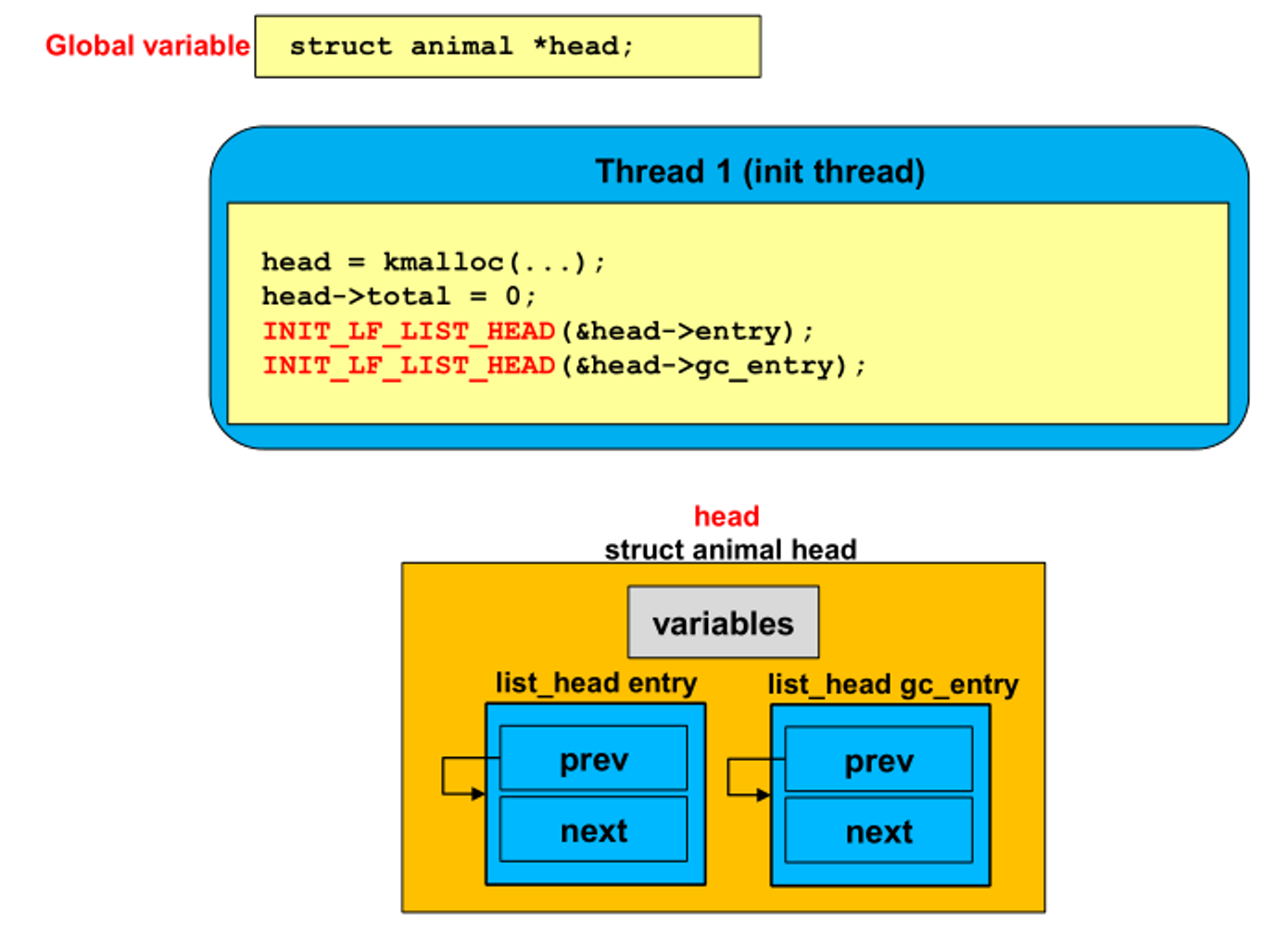
- 전역 변수 head 설정
Lock-free insert
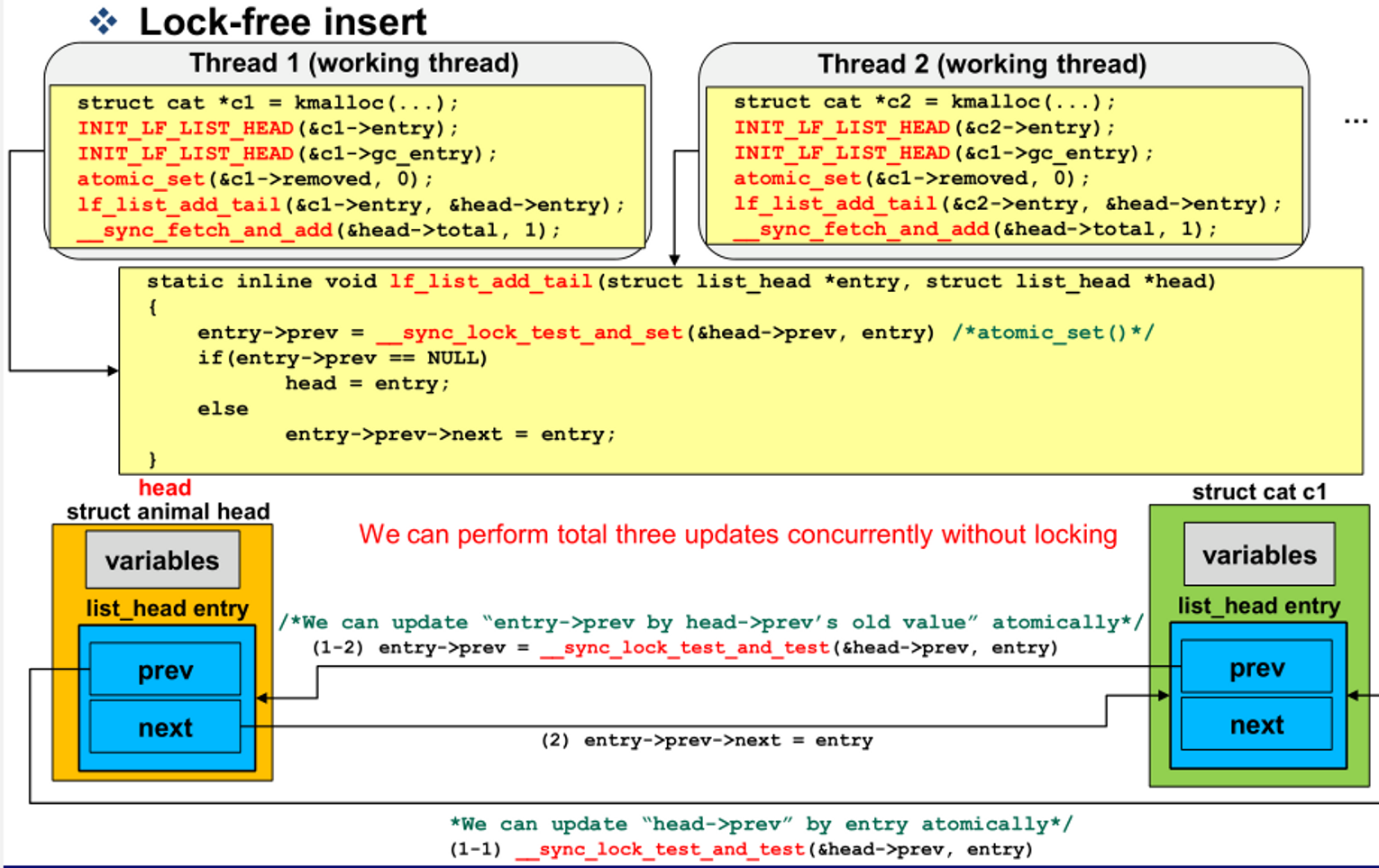
- __sync_lock_test_and_set으로 head의 prev를 추가할 node로 변경
- 이전 값을 추가할 node의 prev에 대입
- 추가할 node의 prev의 next를 추가할 node로 변경
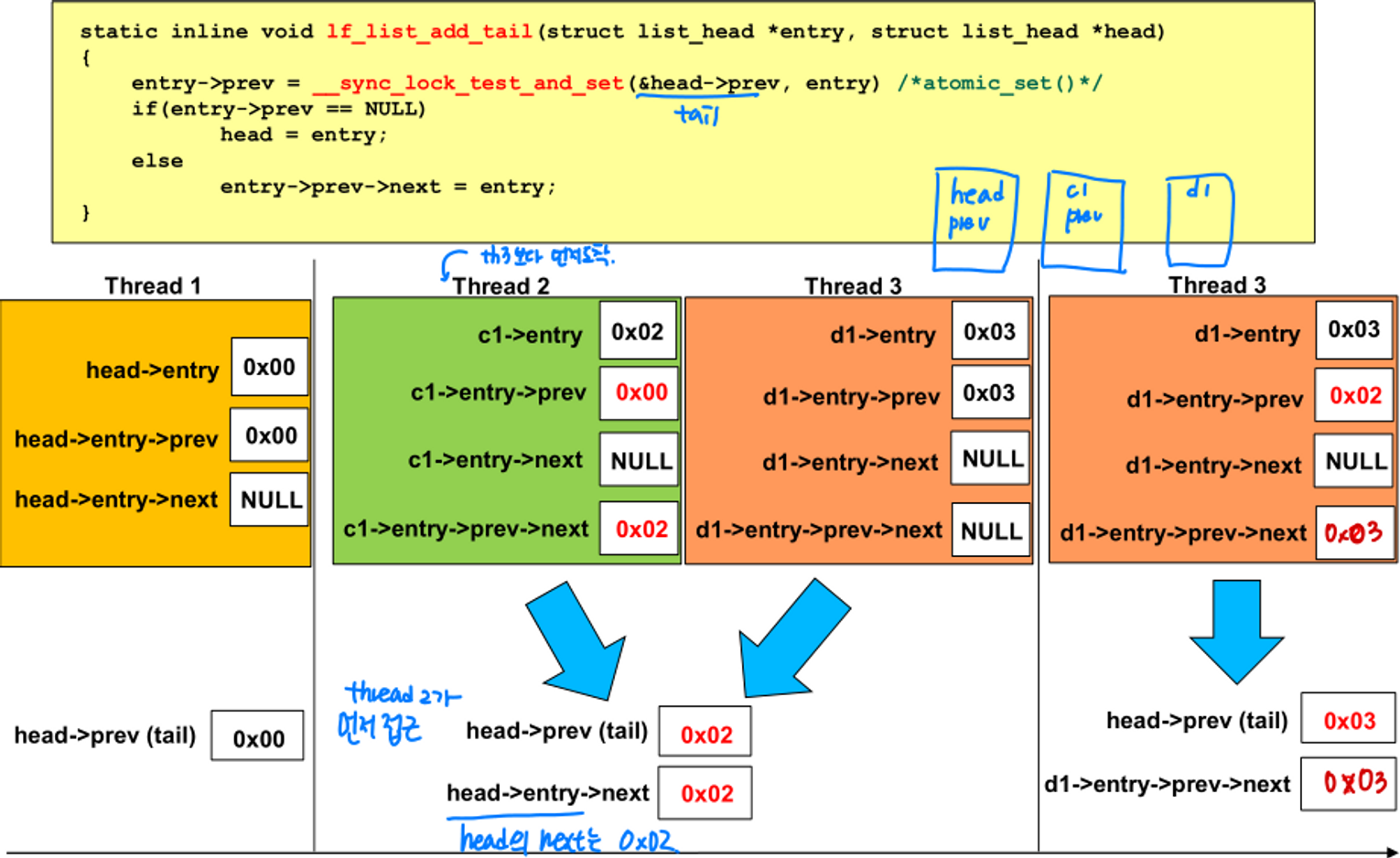
- thread2가 먼저 접근했다고 했을 때, head→prev(tail)는 0x02로 변경되고, head의 next도 0x02로 변경된다.
- thread3은 해당 과정에 접근할 수 없다. (연산이 atomic하게 이루어지기 때문)
- thread3가 접근하여 head→prev와 d1→entry→prev→next를 변경한다.
lock-free delete
- 먼저 entry를 logical하게 삭제하고, garbage collection list를 사용한다.
- logical하게 삭제된 entry는 entry 사이의 connection에 사용된다.
- operation(event) 나 idle time 후에 다른 thread가 entry에 access하지 않는지 확인한 후, entry를 physical하게 삭제한다.
- Ex. task exits, transaction is commited, file I/O 완료
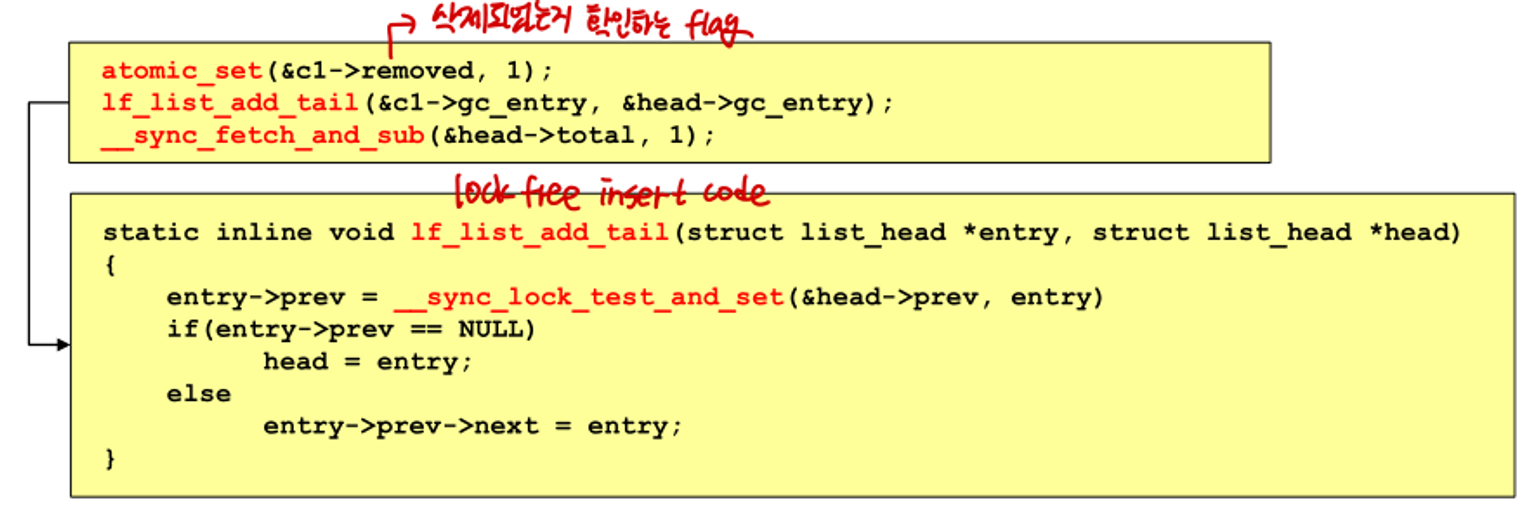

- garbage collection list를 entry가 이미 삭제되었는지 아닌지 확인하기 위해 사용한다.
- garbage collection list를 통해 구조체를 physical하게 free할 수 있다.
lock-free search
- linked list의 entry를 inter entry를 사용하여 탐색한다.
- entry가 linked list에서 삭제되는 것 아님
- entry를 선택할 때 double check
- 삭제된 entry인지 아닌지
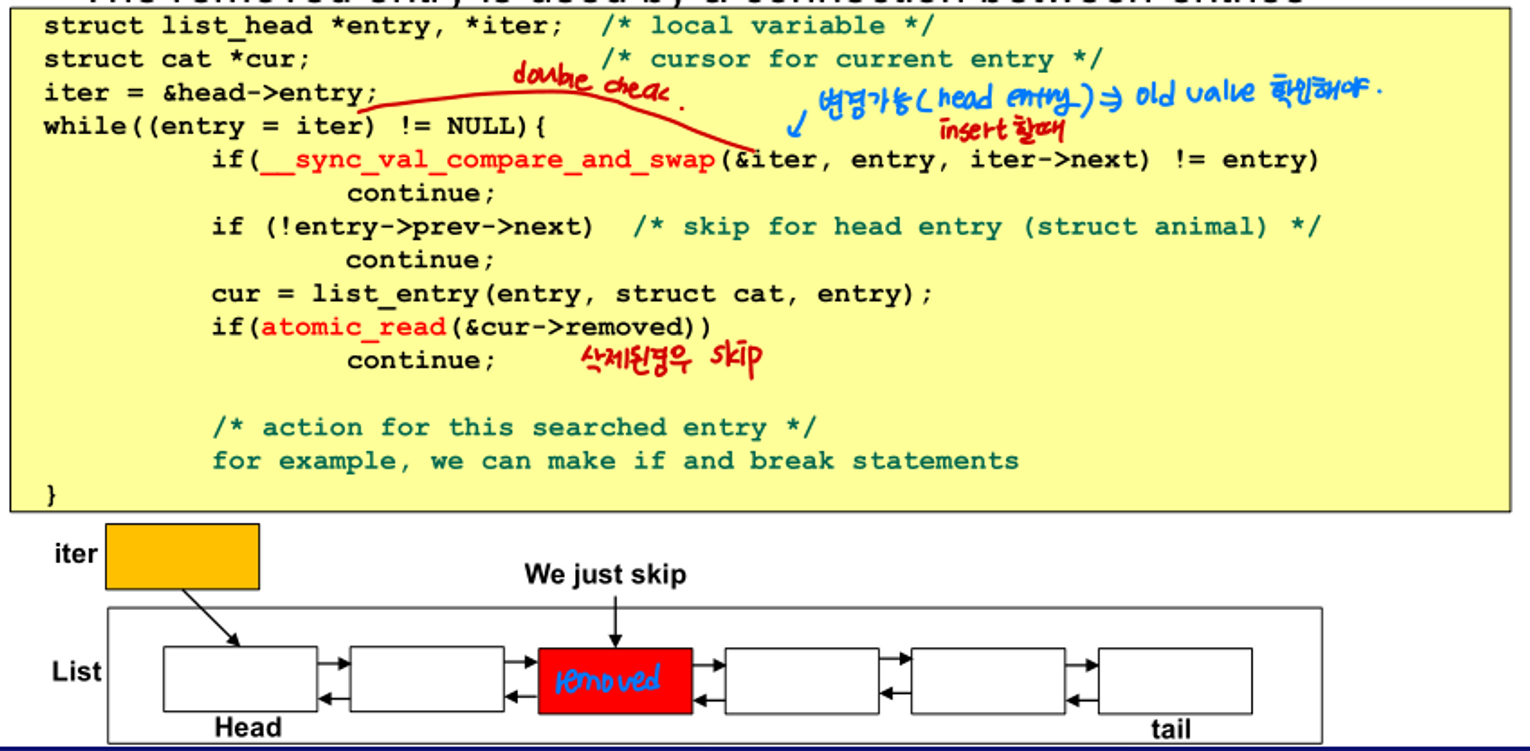
using sentinel nodes (dummy nodes)
- sentinel node는 linked list에서 사용되는 특별한 node
- sentinel node를 사용하여 head, tail 초기화
- list operation은 sentinel node로 수행된다.
- 특별한 head entry는 존재하지 않고, FIFO 방식과 마찬가지로 먼저 도착한 entry가 head entry가 된다.
empting garbage collection list
- linked list item을 physical하게 삭제할 수 있다.
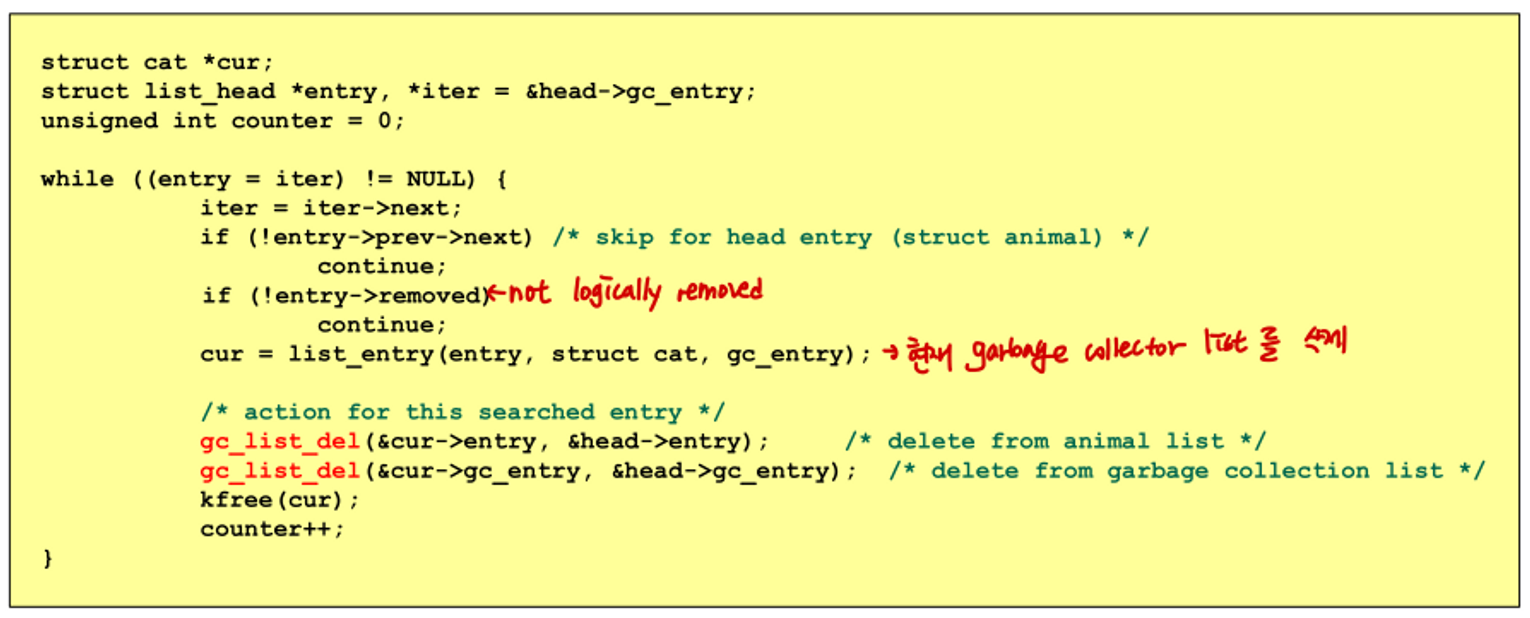
- logical하게 삭제된 것만 physical하게 삭제

728x90
'School Lecture Study > Linux System Application Design' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 리눅스 커널 분석 - Mutex (0) | 2023.01.27 |
|---|---|
| 9. Memory Management (0) | 2022.12.20 |
| 7-4. Task Scheduling in Linux (4) (0) | 2022.12.20 |
| 7-3. Task Scheduling in Linux (3) (0) | 2022.12.20 |
| 7-2. Task Scheduling in Linux (2) (0) | 2022.12.20 |