728x90
중앙대학교 3-2 리눅스 응용 설계 (손용석 교수님) 과목 정리입니다.
From a Program to a Process
Program

- sequence of instructions + data + metadata for program loading and execution
Process in Linux
- Process means “running program”
- system에서 현재 실행되고 있는 program
- whenever program / command is executed / issued in linux, it creates / starts a new process
- pwd 가 실행되면 process가 시작된다.
- Linux는 5자리 ID 번호로 process를 기록 → PID (process ID)
- system의 각 process는 unique PID를 갖는다.
- 사용된 PID는 새로운 process에서 재사용될 수 있다.
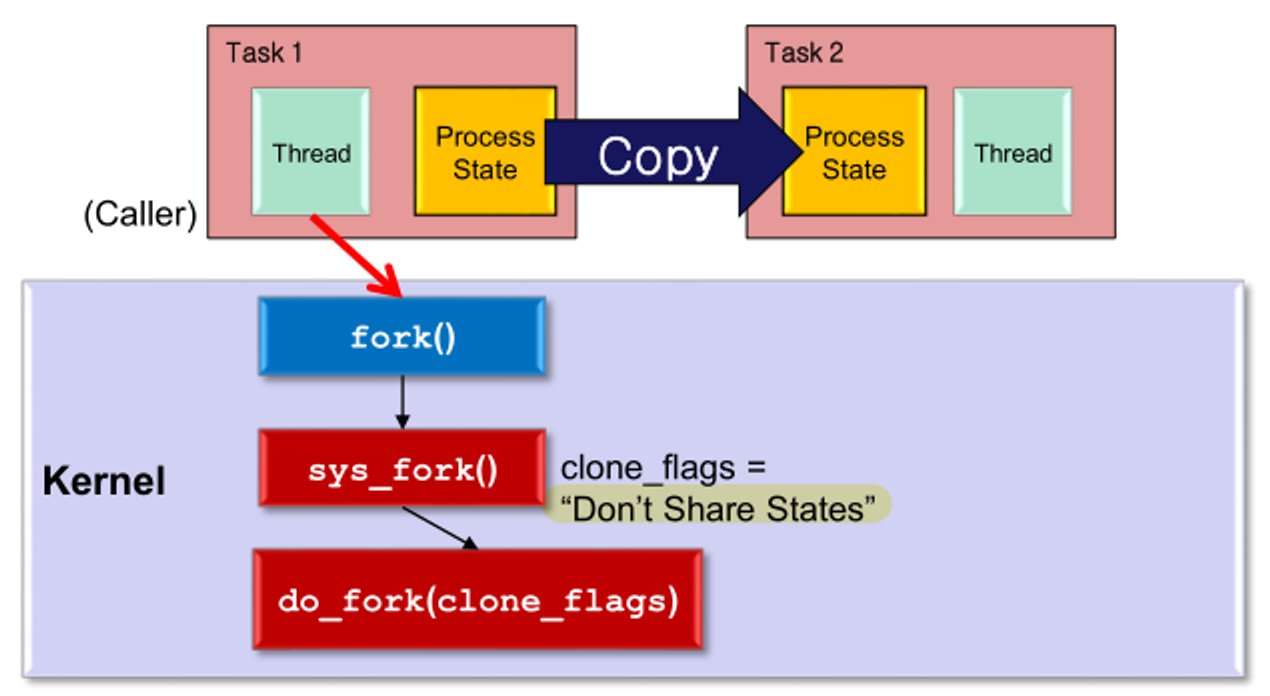
Creating process in user-level
fork system call
- process 자신 : parent process
- 복사된 process : child process
- fork() system call을 사용하여 process 생성
- fork() fail → return -1
- fork() success
- return 0 to child
- return new process id to parent process
Example of fork system call
- fork()의 값으로 parent, child process를 구분

Process descriptor : task_struct (in Linux)
- kernel은 process의 list를 task list라 불리는 circular doubly linked list에 저장한다.
- task의 각 element는 process descriptor이다. (linux/sched.h 에 선언)
- struct task_struct 는 specific process의 모든 정보를 포함한다.
- Managing a process as a task via struct task_struct

- stack : memory stack
- cpus_allowed : 어떤 task가 어떤 CPU에서 실행될 것인지 결정
- mm : task의 주소
- parent : task의 parent
- children : task의 children list
- sibling : task의 sibling list
Process states (in Linux)

Process states
- TASK_RUNNING
- The process is runnable
- 현재 running task이거나 runqueue에서 실행되기를 기다리리는 process
- user- or kernel-space의 task 모두 가능
- TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE
- process is sleeping ( = it is blocked) waiting for some condition
- waiting condition이 true가 되었거나, signal을 받았을 때 kernel이 process 의 state를 TASK_RUNNING으로 설정
- TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE
- sending signal이 process를 깨우지 않는 것만 제외하고 TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE과 동일
- interruption없이 process가 무조건 기다려야 할 때 사용
- TASK_STOPPED
- process 실행이 멈출 때
- running, waiting 둘 다 아닐 때
- task가 어떤 signal을 받을 때 process를 멈출 때 발생
- process 실행이 멈출 때
Manipulating the current process state
- kernel이 set_current_state(task, state) or set_task_state(task, state)를 사용하여 process의 state 변경
Example (Producer-Consumer)
- Producer
- event 발생시키고, consumer 깨우기
- Consumer
- event가 있는지 확인
- list의 모두 보류중인 이벤트 처리
- 아니면 producer가 consumer를 깨울 때까지 sleep

Procedure of Task Creation in Linux

fork()
- caller task의 모든 state를 copy한 task 생성
clone()
- caller task의 일부 state만 공유하는 task 생성
- fork와 다르게 child process가 calling process의 execution context의 일부를 공유하도록 허용한다. (memory space, file descriptors 등)

clone flags

- CLONE_VM
- set : calling process, child process가 same memory space에서 실행
- not set : clone이 일어날 때 child process가 calling process의 memory space의 separate copy에서 실행
_do_fork()
Main procedure in fork
- current task를 복사한 new task 생성
- 새로운 PID 할당
- 생성된 task wakeup

Execution flow

- Check flags
- clone_flag가 invalid combination인 경우 error 리턴
- CLONE_SIGHAND는 CLONEVM이 unset된 상태로 set 될 수 없다.
- Duplicate task_struct
- parent의 값 복사

- check resource limits
- resource가 limit을 초과한 경우 error
- Ex. 지정된 UID에 허용되는 최대 작업 수
- resource가 limit을 초과한 경우 error
- initialize task_struct
- process relationships, scheduling statistics, other variables
- Call sched_fork()
- Scheduler-specific initialization
- Ex. CFS가 parent의 남은 time slice를 child에게 분배

Sharing vs copying state “ABC”

Copy-on-Write
Copying address space
- 모든 page frame을 copy하는 것은 시간이 너무 오래 걸림
- ⇒ Copy-on-Write (COW) 사용

Copy-on-write (COW)

- Optimization technique for copying resource
- 실제 copy operation은 owner가 resource를 수정할 때까지 지연된다.
- kernel의 많은 곳에서 사용 (fork, file systems, virtual memory, etc)
COW in do_fork()

- actual write operation은 하지 않으니까 page frame은 share

- parent나 child 둘 중의 하나라도 처음으로 값 수정이 일어난다면 그 때 page frame이 복사된다.
Code level analysis of _do_fork()

PID namespace
PID namespace
- PID namespaces isolate the process ID number space, meaning that processes in different PID namespaces can have the same PID
- container 내부의 process가 동일한 PID를 유지하는 동안 container의 process sets을 일시 중단/재개하고 container를 새 호스트로 migration합니다.
- 새로운 PID namespace의 PID들은 독립된 system 처럼 1부터 시작한다.
- fork(2), vfork(2), clone(2)를 호출하면 namespace 내부에서 unique한 PID를 갖는 process를 생성한다.

Code level analysis of _do_fork()

- copy_files
- child를 위해 열린 파일들의 정보를 관리하는 files_struct structure 생성
- parents의 file_struct의 내용을 child로 복사한다.
- CLONE_FILES flag를 사용하면 copy하지 않고 structure를 공유하고 reference count를 증가시킨다.
- copy_fs
- root와 current directory들을 관리하는 fs_struct structure를 생성한다.
- parents의 fs_struct 복사
- CLONE_FS flag를 사용하면 복사하지 않고 structure 공유하고 reference count 증가
이하 동일
Signal

Ctrl+C sends signal (SIGINT)

- Ctrl+C를 누르면 interruptHandler 호출 → 종료
_do_fork() - copy_files()
- parent task의 열려있는 file들을 child task로 복사

- oldf : parent의 files
- CLONE_FILES flag가 있으면 복사하지 않고 reference count만 증가 후 함수 탈출
- dup_fd : 새로운 files 구조체를 할당하고 parent의 files 구조체의 내용을 복사해서 새로운 files 구조체에 복사한다.ㅇ
- tsk→files = newf: 새로 만들어진 task(child)의 files를 업데이트한다.

- newf: files_Struct allocate
- spin_lock 실행 (file 보호)
- old_fdt : parent task가 열려 있는 파일들을 저장한 fdtable을 가져온다.
- old_fds : fdt의 file array를 가져온다.
- old의 file수 만큼 new로 파일을 복사한다.
- 복사가 끝나면 spin_unlock 호출
_do_fork() - copy_fs_struct()
- fs_struct는 root directory 와 working directory를 관리한다.

- fs : 새로운 fs_struct를 slab allocator를 사용하여 할당
- spin_lock (다른 thread가 file 변경하지 못하도록)
- root / pwd directory path 할당 → 빈번하게 사용되는 경로이므로 변수에 저장해놓는 것
- path_get : directory entry와 vfsmount location의 reference count를 증가시킨다.
- spin_unlock (lock release)
_do_fork() - copy_sighand()

- CLONE_SIGHAND : flag가 enable되면 복사하지 않고 공유. reference count 1 증가
- refcount_set : sig→count를 1로 초기화한다.
- spin_lock_irq : irq가 siglock에 접근하지 못하도록 lock
- memcpy로 parent의 sighand를 child의 sighand로 복사
- spin_unlock_irq : lock release
Thread
General concept of thread
- a thread is a basic unit of CPU utilization, consisting of a program counter, a stack, and a thread ID
- a thread is part of execution within a process
- process는 여러 개의 threads를 가질 수 있다.
- multithreading?
- thread는 lightweight process
- process를 multiple threads로 나눠서 병렬화를 달성하기 위함
- threads are concurrent flows of execution belong to the same program sharing the same address space
- address space를 process와 공유함

Creating thread in User-level
- Create a new thread
- pthread_create(pthread_t thread, const pthread_attr_t attr,
void *(start_routine)(void**), void *arg)- calling process에서 새로운 thread를 생성하는 함수
- 새로운 thread는 start_routine을 호출하면 실행된다.
- pthread_create(pthread_t thread, const pthread_attr_t attr,
- Join with a terminated thread
- pthread_join(pthread_thread, void **retval)
- thread가 지정한 thread가 종료될 때까지 기다린다.
- failure to join with a thread that is joinable, produces a “zombie thread”
- zombie thread는 일부 system resource를 사용한다.
- pthread_join(pthread_thread, void **retval)
- Linux kernel은 pthread에 대해 clone() system call을 사용한다.
Creating thread - Code

- pthread_create를 사용하여 thread 생성
- pthread_t : thread ID를 나타내는 type
- pthread_self() : thread ID를 return하는 함수
- child thread 생성하고 tid_print로 PID 출력하기
- tid_print가 끝나기를 기다림
Kernel thread is used to perform backgrond operations in the kernel
Ex. Daemon
Ex. kswapd, journald
→ user level thread와 매우 비슷하다.
→ 각 thread가 각각의 schedulable entity를 갖는다.
⇒ kernel thread를 생성하기 위해서는 kthread_create를 사용한다.
Kthread APIs
- Creation APIs
- kthread_create(threadfn, data, namefmt, arg...)
- create a kernel thread
- kthread_run(threadfn, data, namefmt, ...)
- create a kernel thread with checking correct creation
- kthread_create(threadfn, data, namefmt, arg...)
- Stop APIs
- kthread_stop(struct task_struct *k)
- stop (terminate) a created kernel thread
- kthread_should_stop()
- check a kernel thread to decide continue or stop (terminate)
- kthread_stop(struct task_struct *k)
Example



- kthread_should_stop : thread가 멈출때까지 실행
728x90
'School Lecture Study > Linux System Application Design' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 6-2. Synchronization (2) (1) | 2022.12.20 |
|---|---|
| 6-1. Synchronization (1) (0) | 2022.12.20 |
| 4-2. Kernel module (1) | 2022.12.19 |
| 4-1. Design Principle of Linux Kernel (0) | 2022.12.19 |
| 3-2. System calls (0) | 2022.12.19 |