728x90
중앙대학교 3-2 리눅스 응용 설계 (손용석 교수님) 과목 정리입니다.
Processor Modes
- The OS must restrict what a user process can do
- What instructions can execute
- What portions of the address space are accessible
- Supervisor mode (Kernel Mode)
- instruction set의 어떤 instruction이든 실행 가능
- processor 중지, mode bit 변경, I/O 초기화
- system의 어떤 memory location이든 접근 가능
- OS address space의 code & data
- instruction set의 어떤 instruction이든 실행 가능
- User Mode
- Restricted capabilities
- privileged instruction 실행 불가
- kernel address space 내부의 reference code & data를 직접 참조 불가
- Any such attempt results in a fatal “protection faults”
- Instead, user mode access OS code and data indirectly via system calls
- Restricted capabilities
System call

- system call is the programmatic way in which a computer program requests a service to the kernel of the operating system it is executed on
- compuiter program은 operating system’s kernel에 요청할 때 system call을 생성할 수 있다.
- System call은 OS의 service를 user program에 Application Program Interface (API)를 통해 제공한다.
- API는 process와 OS 사이의 interface를 user-level process가 OS의 service를 요청할 수 있도록 허용한다.
- System call은 trap의 special version
- Trap is a software interrupt
Interrupt
Concept
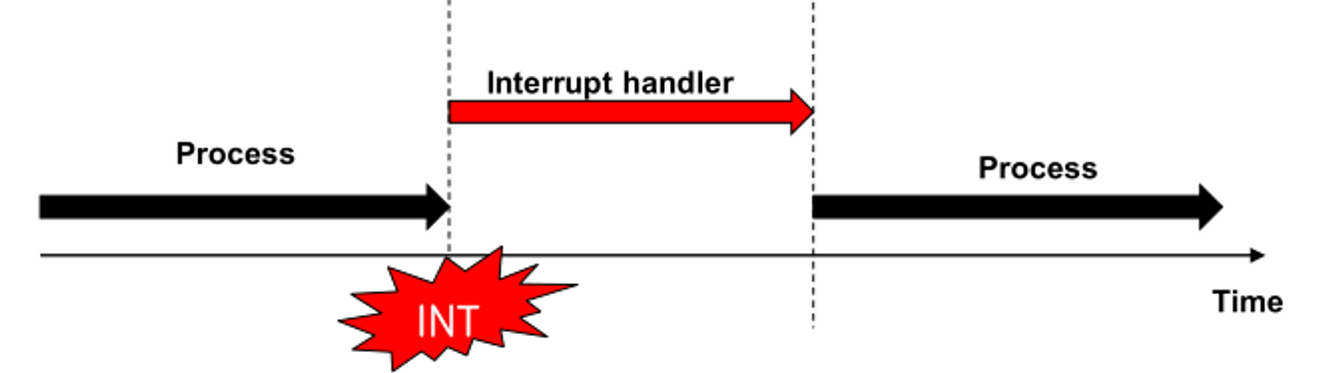
- An interrupt is an event indicating the need for change in execution
- 인터럽트는 실행 변경의 필요성을 나타내는 event.
- interrupt는 event가 제때 처리될 수 있도록 processor가 현재 실행 중인 코드를 interrupt하기 위한 요청
- request accepted : processor는 current activity (current process)를 멈추고, current activity (current process)의 state를 저장한 후 event를 처리하기 위해 interrupt handler에 의해 호출된 function을 실행한다.
- interrupt handler가 끝난 후에, 중지되었던 acitivity가 재개된다.
- Example

Trap and System call
Trap
- Trap is a synchronous software interrupt
- Trap is no wait
- Trap 은 user process에 의해 발생하고(System call), OS의 functionality를 호출한다.
- Trap 은 다양한 요인으로 발생할 수 있는 software-produced interrupt
- including instruction error (division by zero, illegal memory access)
- Trap은 또한 user program이 OS에 서비스 요청(System call)을 할 때 생성될 수 있다.

Example

printf(”%s\n”, str); 을 호출했을 때
- printf() : C 라이브러리에서 함수를 호출하기 위해 user space에서 사용가능한 APIs / interfaces
- printf()는 write() system call을 사용한다.
- write() system call은 data를 output으로 내보내는 역할을 한다.
Trap vs Interrupt

Trap
- user program이 OS에 특정 functionality를 즉시 수행하도록 지시하는 signal
- synchronous process
- 모든 trap은 interrupt
- software interrupt로 불림
- user program instruction이 trap을 발생시킴
- OS의 특정 functionality를 실행하고, trap handler에게 제어권을 넘김
Interrupt
- immediate attention이 필요한 event를 나타내는 hardware에서 CPU로 전송되는 신호
- asynchronous process
- 모든 interrupt가 trap인 것은 아님
- Hardware device에 의해 생성됨
- hardware interrupt로 불림
- CPU가 특정 interrupt handler routine을 실행하도록 강제함
System call procedure
x86 architecture의 interrupt vector table을 구현하는 자료구조

- System call in terms of user and kernel space

System call
- open, read, write, close, wait, exec, fork, exit, kill
System call category
- Process control
- File management
- Device management
- Information mainteneance
- Communication
- Protection

Example of Linux System calls
Fork()

- creates a task by copying all the states of the caller task
- 두 process는 상태를 공유하지 않음
clone()

- creates a task that shares a subset of states of the caller stack
- 일부 state를 공유한다.
Implementation of do_fork()

- do_fork()
- call copy_process() : actual copy operation 실행
- allocate a new PID
- call wake_up_new_task() : runqueue의 head에 새롭게 생성된 task를 두기
- Sched_class
- Real Time : enqueue_task_rt
- Normal : enqueue_task_fair
728x90
'School Lecture Study > Linux System Application Design' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 6-1. Synchronization (1) (0) | 2022.12.20 |
|---|---|
| 5. Process and Thread (0) | 2022.12.20 |
| 4-2. Kernel module (1) | 2022.12.19 |
| 4-1. Design Principle of Linux Kernel (0) | 2022.12.19 |
| 3-1. Linux Commands and Tools (0) | 2022.12.10 |